LED lighting strips function by utilizing light-emitting diodes (LEDs) that produce light when electricity passes through semiconductor materials. These strips provide comprehensive, versatile, and customizable lighting solutions for various applications. Different types of LED diodes affect brightness and color accuracy, typically installed on flexible circuit boards powered by printed circuit boards (PCBs) to distribute electricity uniformly. Current-limiting resistors help regulate voltage, ensuring the safe and long-lasting operation of LEDs. The light output of LED strips is determined by LED density and the semiconductor material used. To gain a deeper understanding of how LED lighting strips work and the advantages they offer, it is recommended to explore the complex components and mechanisms that drive their efficient performance.
Key Takeaways
- LED diodes on flexible PCBs emit light with electricity.
- Current-limiting resistors regulate voltage for safe operation.
- Semiconductor materials determine light color and brightness.
- Energy-efficient design minimizes heat production.
- Versatile for various applications due to customizable features.

Yiliaw 44 Keys IR Remote Controller Kit – Includes Wireless Rectifier Control Box and DC 12V 3A Power Supply Adapter – Replacement Control for SMD 5050 3528 2835 RGB LED Strip Lights
⚠NOTE⚠(1)Compatiable with 12V LED Strip Lights ONLY. (2)Only for RGBW strips which has 4-pin connectors. (3)Connect box output…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
LED Strip Light Components
LED strip light components consist of various elements essential for their functionality and durability. These components include LED diodes, printed circuit boards (PCBs), vital current-limiting resistors, protective casings, and adhesive backing.
The LED diodes are the core of the strip, emitting light when electricity passes through them. The PCBs play a vital role in distributing electricity evenly across the strip to power the LEDs efficiently. Current-limiting resistors are integrated into the strip to regulate voltage, safeguarding the LEDs from potential damage caused by fluctuations in electricity.
Protective casings are employed to shield the components from external factors such as weather conditions, dust, and impacts, ensuring the longevity and durability of the strip. The adhesive backing facilitates easy installation of the strip in various locations, making it a versatile lighting solution for both residential and commercial settings.
Together, these components work harmoniously to deliver bright and energy-efficient lighting solutions for a wide range of applications.

KSIPZE 100ft Led Strip Lights RGB Music Sync Color Changing Led Lights with Smart App Control Remote Led Lights for Bedroom Room Lighting Flexible Home Décor
APP and IR Remote Contorl: With a stable connection,control your LED lights,freely change in 16 million colors,adjust brightness,customize…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
LED Diodes
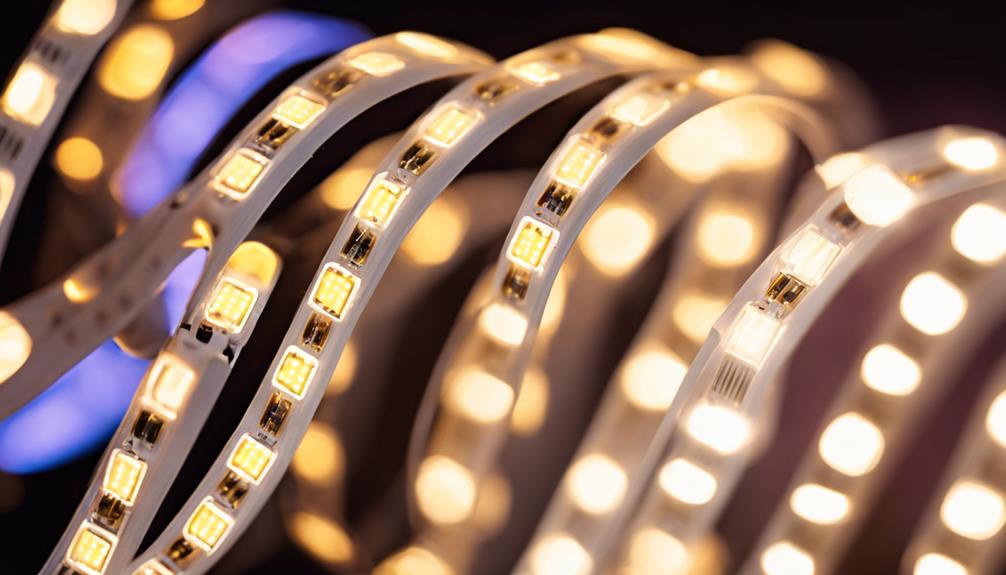

A key component in modern lighting technology, semiconductor devices known as LED diodes emit light when an electrical current passes through them. These diodes come in various sizes and types, affecting the brightness, color accuracy, and overall energy efficiency of the lighting strip.
Different semiconductor materials within LED diodes determine the color of light they emit, ranging from red, green, blue, to white. LED diodes are highly energy-efficient, converting a greater percentage of electricity into light compared to traditional lighting sources.
When placed on a flexible circuit board, LED diodes allow for customizable lighting solutions, enabling users to create different colors and patterns for various applications like ambient lighting, accent lighting, or task lighting. The versatility and efficiency of LED diodes make them a popular choice for a wide range of lighting needs.

DAYBETTER Led Strip Lights Waterproof, 32.8ft(2 Rolls of 16.4ft) Led Tape Lights Color Changing 300 LEDs Light Strips Kit with 44 Keys Ir Remote Controller and 12v Power Supply for Indoor Outdoor Use
Using resin as a material makes the light strip waterproof, not only for indoor use, but also outdoor…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Printed Circuit Board
In modern lighting technology, the printed circuit board (PCB) plays a vital role in distributing electricity to the LEDs in lighting strips. PCBs feature copper traces that efficiently conduct electricity to power the LEDs. These slim and flexible boards allow for easy customization and cutting of the strip to desired lengths.
Within the PCB, current-limiting resistors are integrated to regulate voltage and protect the LEDs from damage. Proper alignment of copper pads and connectors on the PCB is vital when joining multiple LED strips to guarantee the continued functionality of the lighting system.
The PCB fundamentally acts as the central hub that organizes and delivers electrical power to the individual LEDs, enabling them to emit light. Its design and components are meticulously crafted to optimize the performance and longevity of LED lighting strips while maintaining energy efficiency and safety standards.

FSJEE 4 Pin LED Strip Connector Kit for 5050 RGB(NOT RGBIC) 10mm LED Light Strip,Include 8 Types of Solderless Accessories,Provide Most of Parts for DIY Lighting Project
Application: 4pin 10mm LED quick connector kit suitable for 10mm wide SMD 5050 RGB(not RGBIC) LED ribbon lights,connecting…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Current-Limiting Resistors

Current-limiting resistors play an important role in regulating voltage to safeguard LEDs in lighting strips from excessive current flow.
- Voltage Regulation: These resistors help regulate the voltage supplied to each LED, ensuring a safe operating range and preventing damage from overcurrent.
- Excess Current Protection: By limiting the amount of current flowing through the LEDs, these resistors protect the components from potential harm caused by excessive current flow.
- Importance of Resistance Value: The resistance value of the resistor is vital as it determines the current passing through the LED, directly impacting its brightness and longevity.
- Consistent Brightness and Longevity: Properly sized resistors ensure that each LED receives the right amount of current for consistent brightness and extended lifespan, contributing to the overall efficiency and safety of the LED lighting strip. Calculating the correct resistor value is essential for maintaining peak performance and ensuring the longevity of the LEDs.
Light Production Mechanism

When electricity passes through the semiconductor materials in LED lighting strips, light is produced as electrons release energy in the form of photons. This process is what enables LED lighting strips to illuminate spaces efficiently.
The specific semiconductor materials used in the LEDs determine the color of the light produced, offering a range of options for different lighting needs.
Additionally, the brightness and uniformity of the light can be influenced by the LED density on the strip; higher density typically results in brighter and more evenly distributed light.
One of the key advantages of LED lighting strips is their energy-efficient nature. Unlike traditional lighting sources, LEDs convert a higher percentage of the electricity they receive into light rather than heat, making them a more sustainable lighting option.
Understanding the light production mechanism of LED lighting strips helps users appreciate their versatility and effectiveness in various applications.
Installation Tips

As users prepare to install LED lighting strips, guaranteeing a clean and dry mounting area indoors is vital for proper adhesion and longevity. Here are some installation tips to take into account:
- Use Mounting Clips: Employ mounting clips or tracks for a secure and permanent installation, especially in high-traffic areas or where vibrations may occur.
- Align Copper Pads: When joining LED strips, align copper pads and connectors to avoid damaging the circuitry and ensure a proper electrical connection.
- Utilize Waterproof Casings: For outdoor installations, use waterproof casings to shield LED strips from weather elements and enhance their lifespan.
- Ensure Proper Adhesion: Proper placement and adhesion of LED strips are essential to prevent peeling or detachment due to weather impacts or environmental factors.
Powering LED Strips

LED strips necessitate a compatible power supply voltage to guarantee peak performance and prevent damage. Typically, these strips operate on either 12V or 24V DC power. It's important to match the power supply voltage to the LED strip voltage to avoid any potential damage.
When connecting multiple LED strips in parallel, ensuring a suitable power supply is essential to prevent voltage drop issues. Additionally, correct polarity connection of wires is crucial to prevent LED damage and ensure proper functioning.
To enhance the customization and control of LED strip lighting effects, using an LED controller is recommended. By carefully considering power requirements, maintaining the correct voltage, preventing voltage drops, and ensuring proper polarity connections, users can optimize the performance and longevity of their LED lighting strips.
Benefits of LED Lighting Strips

Utilizing LED lighting strips presents a variety of advantages that cater to efficiency, longevity, safety, versatility, and ambiance enhancement.
- Energy-efficient: LED lighting strips consume much less power compared to traditional incandescent bulbs, with savings of up to 90% on electricity bills.
- Long-lasting: Quality LED strips can operate for over 50,000 hours continuously while maintaining consistent light output, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Safe and low voltage: LED strips emit minimal heat, making them safe for various applications, including confined spaces, and operate at low voltage levels for added safety.
- Versatile and vibrant lighting: The flexible nature of LED strips allows for easy installation in diverse environments, while offering bright and vibrant lighting that enhances the ambiance of any space.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do LED Strip Lights Need to Be Plugged In?
LED strip lights do require plugging in to a power source for operation. They typically need a 12V or 24V DC power supply to function properly.
Connecting the power supply to the LED strip lights provides the necessary voltage for illumination. Ensuring proper connection is essential for consistent and reliable lighting.
LED strip lights can be easily plugged into compatible power sources, offering quick and convenient setup for users.
What Are the Disadvantages of LED Light Strips?
LED light strips come with drawbacks that should be taken into account. They can be more expensive upfront than traditional lighting. Some LED strips offer limited color choices and may struggle with color accuracy.
Heat dissipation issues can impact their lifespan and performance. Additional accessories like controllers or dimmers might be necessary for full functionality.
Compatibility problems with existing fixtures or wiring can arise during installation, potentially complicating the setup process for LED light strips.
How Do LED Strip Lights Connect to Power?
LED strip lights connect to power through a compatible 12V or 24V DC power supply. Maintaining proper polarity when connecting wires is essential to prevent damage.
Connecting multiple LED strips in parallel to a suitable power supply guarantees even power distribution. Limiting the strip length prevents excessive voltage drop.
Using an LED controller allows customization of lighting effects.
How Are LED Strips Controlled?
LED strips are controlled by microcontrollers like Arduino, Raspberry Pi, or dedicated LED controllers. These controllers send digital signals to the LED strips, dictating color and brightness for each LED. Digital LED strips have integrated ICs that receive data signals to control individual LEDs.
Common protocols like WS2811 or WS2812 are used to communicate data. Control software or programming enables users to create custom lighting effects, patterns, and animations on LED strips.
Conclusion
To sum up, LED lighting strips are like tiny superheroes, illuminating your space with precision and efficiency.
With their powerful diodes and current-limiting resistors, these strips work together to create a dazzling light show.
So, next time you're looking to add some pizzazz to your room, remember that LED lighting strips are here to save the day!



